Sometimes just learning the jargon of a specific technology and/or process is half the battle. If you are new to SAP Integrations or a seasoned SAP Integration Professional, it can be beneficial to go back to basics. Take a look at our take of the main terms, phrases and acronyms for the world of SAP Integrations. Let’s call it the SAP Integration Alphabet or the “ABCs” of SAP Integration.
What are SAP Integrations?
SAP Integrations are designed to ensure proper communication between SAP and non-SAP applications in a business and ensures the data that moves between those applications or processes are done successfully, accurately and securely. This process of integrations is necessary for a lot businesses since SAP is a widely used piece of software for different business functions including HR, logistics, CRM and accounting which has made SAP one of the largest software companies in the world.
Changing Terminology
The changing of names or terminology is the nature of the beast in most industries especially in technology. That is no different for SAP Integration and recently SAP Cloud Platform Integration (CPI) was renamed to SAP Cloud Integration (which is now part of the larger SAP Integration Suite) and that rebrand by SAP goes beyond the application and tool name changes but that is for a different discussion.
Because of the constant change in terminology suggested by SAP and other professionals who work with SAP products, it can be good to refresh ourselves on the current lingo being said by SAP Integration Experts and SAP themselves.
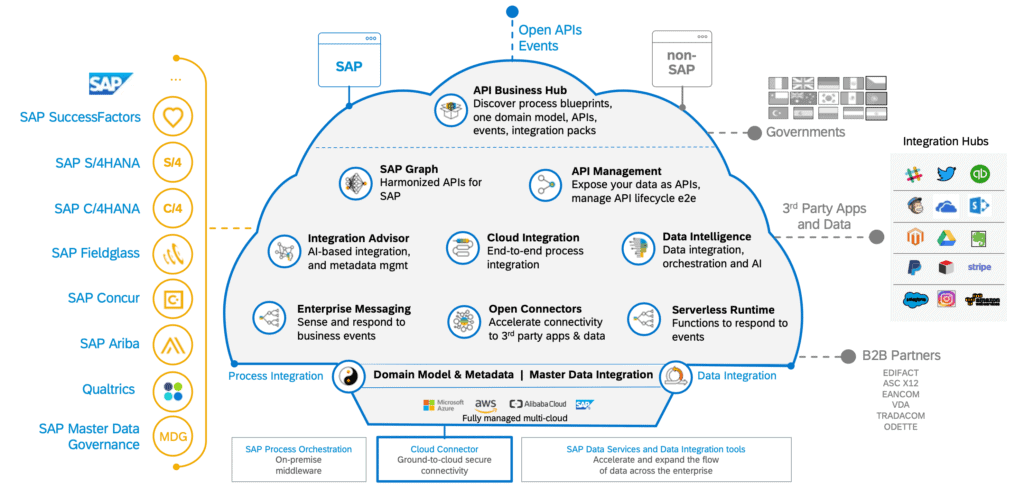
The “ABCs” of SAP Integration
Artifact – Any piece of data that is part of an integration.
Endpoint – An application that is the destination of data in an integration.
Integrated Configuration Object (ICO) – A file that defines the end-to-end flow like source system, channel and target system and this is important for end-to-end message flows and defines the message flow.
IFlow (Integration Flow) – An object that creates the configuration object in the same database of the Integration Directory which will allow for you see the Integrated Configuration, Business Components and communication channels.
Integration – The process of exchanging data between two separate applications to ensure the business processes run smoothly.
Landscape – A term to describe all your business systems that are connected into groups. There will be a development environment where you have all the same applications as there is in the production environment.
Message Mapping – An object/service that allow you to convert from one XML message to another in a graphical tool. It is one of the cornerstones of the SAP PI platform.
Rollback – The process of reverting back to a previous version of an integration if there are errors in the new integration.
SAP Business Technology Platform (BTP) – A platform formerly known as SAP Cloud Platform (SCP) that delivers cloud applications as SAP’s Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS).
SAP Cloud Foundry – An open-source platform that performs as a Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) and is utilized by the SAP BTP platform to manage multiple cloud applications. It is being deployed at AWS, Azure, Google and Alibaba Cloud. Moreover, Cloud Foundry enables users to build or use applications on the platform.
SAP Cloud Integration (CPI) – A platform formerly known as SAP Cloud Platform Integration that connects together SAP and non-SAP on-premise and cloud applications and is part of the larger SAP Integration Suite.
SAP Integration Advisor – An application within the SAP Integration Suite that assists with the creation and maintenance of content at a business domain level to allow the support of SAP Integration Experts without the need of programming language code.
SAP Integration Suite – A platform that allows for the integration of on-premise, hybrid and cloud-based applications and processes to work together as part of SAP’s Integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS). SAP Integration Suite combines Process Integration, API Management, Integration Advisor and Open Connectors into one cohesive application for managing integrations.
SAP Open Connectors – An application that’s part of the SAP Integration Suite that makes it easier to connect with different types of services generically.
SAP Process Integration (PI) – A platform that integrates SAP and non-SAP applications within an organization and/or between different organizations. A Process Integration only within an organization is seen as “Application-to-Application” and Process Integrations between different organizations is seen as “Business-to-Business”.
SAP Process Orchestration (PO) – An application designed to optimize business processes and combines with the capabilities of SAP Process Integration and thus is seen as an improved or updated version of SAP Process Integration. Moreover, SAP PO adds Process Modelling tools like NW BPM and Rules Management together with business capabilities.
Transports – An apparatus that ensures that any customizations or general changes to an integrated are implemented correctly.
Did we miss any important terms?
There you have it: Our take on the “ABCs” of SAP Integration. How did we do? Did we get them all or did we miss any? Please share this with your colleagues and see what they have to say. We look forward to hearing from the SAP Community about this.

